Search Engineering
Migrating from Solr to Elasticsearch, and their differences
Our migration journey and key lessons from this journey.

After realizing that it took a literal team of engineers to keep our self managed Solr infrastructure up to date and working, we are moving to a managed search solution — Elasticsearch!
Over 2021, we have migrated one of our smaller search indexes fully to Elasticsearch and are currently in the process of using Elasticsearch for some new search domains. The journey so far has taught us a lot about the key differences between Solr and Elastic, as well as the nuances that people may not be aware of unless they go through a similar migration.
We have put together this blog post to help others who are considering such an exercise.
Why would we care about Elasticsearch?
We have been using Solr since 2014 at Canva when it was easily the most established option with the most active community. Now, in 2022, Elasticsearch is no longer the unexciting and somewhat unreliable new kid on the block, but has proven itself to be a reliable search engine with a strong developer community and support.
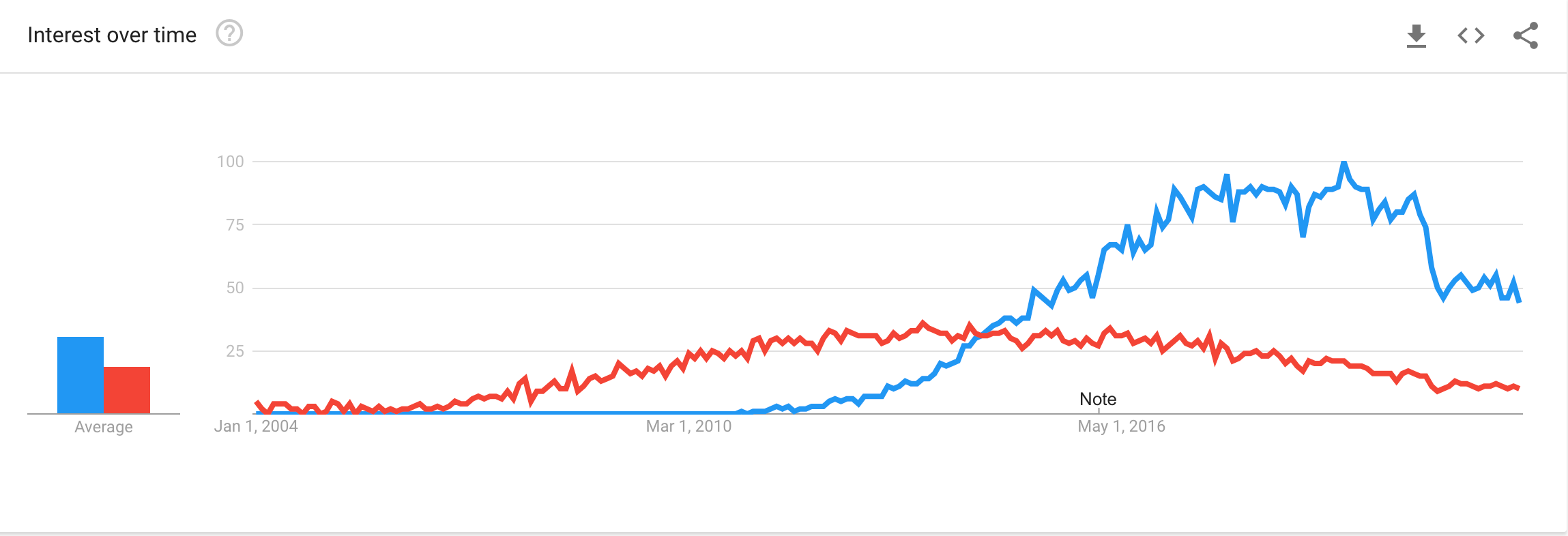
The reasons we started favoring Elasticsearch were:
- An active community and support forum.
- It is now easier to hire engineers with Elasticsearch experience, and harder to hire people familiar with Solr.
- Managing Zookeeper(opens in a new tab or window) is a significant overhead, which adds engineering complexity and failure surfaces.
Side By Side Comparison
The following sections provide side by side comparisons of how we experienced Solr and Elasticsearch, what we like and struggle with from each, and the things we wish we knew about Elasticsearch before the migration. We hope it will benefit teams looking to do the same thing as we did.
Terminology
The table below are terminologies we'll be using in this post.
Solr | Elasticsearch | Definition/Function |
|---|---|---|
Cluster | Cluster | The group of instances that hosts Elasticsearch or Solr |
Zookeeper | Master Nodes | The application/nodes responsible for managing cluster state and leader elections |
Node | Data Nodes | The nodes responsible for indexing, querying, and data storage |
Collection | Index | The search index against which to execute queries |
Schema | Index Template > Mappings | Defines the fields, analyzers and filters for a search index |
Solr Config | Index Template > Settings | Defines a group of settings, such as timeouts and logging defaults, for a collection/Index |
Cluster management
A key difference in how we (as engineers) interact with the technologies is how the infrastructure is managed. Here are aspects to consider.
Security
Solr
- Security group level rules.
- You can't do role based access control without custom authorizers.
Elasticsearch
- Security group level rules.
- Cluster policies for role-based access control (IAM).
- Fine grained access control(opens in a new tab or window) on a cluster.
- Requests must be signed using Sigv4(opens in a new tab or window).
Leaders (and state management)
Solr
- Must be managed separately to Solr. If you're managing Solr, you must also manage Zookeeper(opens in a new tab or window).
Elasticsearch
- Handled by the Master nodes.
- Can be run on the same or a dedicated instance.
Defining shard and placing nodes
Solr
- Shards are defined on collection creation.
- Autoscaling can add nodes to maintain minimum replication, but does not support balancing across AZs (AWS availability zones).
- The autoscaling does not balance replicas to prevent dangerous topologies. We observed several undesirable behaviours of the autoscaling.
- Nodes being assigned as leaders of many shards and crashing.
- Two nodes being assigned as replicas of the same shard resulting in a large load on the survivor if one crash, often also taking out the survivor.
- Adding multiple nodes as replicas to a single leader concurrently causing the leader to try and distribute its data to both new followers at once. This took down the leader occasionally.
- We have some self-managed scripts to ensure that replicas of a shard are in distinct nodes and across AZs, but this is not out of the box.
Elasticsearch
- Shards are defined on Index creation, or specified by an index template.
- Shards are placed on nodes based on a replication value, defined on Index creation, or specified by an index template.
- Shard replicas are balanced across AZs(opens in a new tab or window) (AWS availability zones) by default.
- Shard placement avoids adding replicas of the same primary shard on one node instance.
Index mappings and templates
Solr
There are two files that define a collection:
schema.xml, which contains the analyzers, tokenizers, filters, and field definitions.solrconfig.xml, which contains settings, such as custom default handers, Zookeeper timeouts, and auto commit intervals.
Elasticsearch
You can create indexes using an index template(opens in a new tab or window) with default values for these settings, but changing the template does not change the configuration of live indexes. To change the configuration of a live index, you must apply settings or mappings directly to that index.
Aside - What are Index Templates?
The way Elasticsearch handles the configuration of an index is a big change from Solr. Understanding what index templates(opens in a new tab or window) are and how they can be used helps translate the Solr configuration files to the Elasticsearch context.
Index Templates(opens in a new tab or window) contain the
settings and the mappings that define an index. They specify an index
pattern (such as test-*) that is applied to all new indexes matching
this pattern.
Mappings(opens in a new tab or window) define fields and
the analyzers/tokenizers they should use. Mappings can also be labeled
as "dynamic": "strict", which requires you to explicitly add fields
that are to be indexed to the mapping (like most fields in Solr); if a
document to be indexed contains a field that is not defined in the
mapping, it will fail to be indexed.
Settings define everything else: logging, shards, replication, timeouts, analysers, tokenizers and filters.
You can also create index templates using component templates. For example, different component templates might each define:
- Mappings, analyzers, tokenizers and filters,
- Shards and replication, and
- Logging.
You could then create an index template using these three templates, applying their combined configuration to new indexes.
Defining mappings
Elasticsearch and Solr have similar tokenizers and analyzers but define the schema differently and have their own indexing behaviours.
Solr
<field name="brand" type="simple_text" indexed="true" stored="false" required="false" multiValued="true"/>...<fieldType name="simple_text" class="solr.TextField"positionIncrementGap="100"><analyzer><tokenizer class="solr.WhitespaceTokenizerFactory"/><filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/><filter class="solr.ASCIIFoldingFilterFactory"/></analyzer></fieldType>
Elasticsearch
{"settings": {"analysis": {"analyzer": {"simple_text": {"type": "custom","tokenizer": "whitespace","filter": ["lowercase","asciifolding"]}}}...},"mappings": {"dynamic": "strict","properties": {"brand": {"type": "text","analyzer": "simple_text"}}...}}
Indexing
Solr
- Requires fields to be explicitly defined by a field
name, or as a dynamic field, eg.
title-*. - Must specify whether a field is required.
- Must specify whether a field is multivalued.
- Default shard routing routes on the id specified
before the
!symbol.
Elasticsearch
- Dynamic fields by default, or can set
"dynamic": "strict". - Supports wildcard field types.
- Required and multivalued fields are not enforceable.
- Routing to shards is calculated based on
_id(or_routingif present).
Queries
For most queries, there are direct equivalents between Solr and Elasticsearch, but typically with different labels and query structure;
Solr
- Queries are string based and use
edismax.
Elasticsearch
- API with structured json requests(opens in a new tab or window) in the body of a request.
- Uses a DSL(domain specific language) on Lucene(opens in a new tab or window).
- Can create query templates that have default values.
The Same Variable but a Different Word
Solr
"start" : 0, "rows" : 10
Elasticsearch
"from" : 0, "size" : 10
Solr
"debug": true
Elasticsearch
"explain": true
An Equivalent Filter Query
Solr
defType=edismaxq=title:search, content:elasticsearchfq=status:published, publish_date:["2015-01-01" TO *]
Elasticsearch
GET /_search{"query": {"bool": {"must": [{ "match": { "title": "Search"}},{ "match": { "content": "Elasticsearch" }}],"filter": [{ "term": { "status": "published" }},{ "range": { "publish_date": { "gte": "2015-01-01"}}}]}}}
An Equivalent Field List
Solr
defType=edismaxq=user:kimchyfl=name, id
Elasticsearch
GET /_search{"_source": {"includes": [ "name", "id" ]},"query" : {"term" : { "user" : "kimchy" }}}
Benefits of migrating
Migrating provides additional functionality, such as composite fields and vectors.
Nested Data Type Mapping
Elasticsearch supports mapping object fields as nested data types(opens in a new tab or window). Objects mapped this way capture structured data, and can be queried both individually or as a collection of fields.
Mapping
PUT my-index-000001{"mappings": {"properties": {"user": {"type": "nested","properties": {"first": {"type": "text"},"last": {"type": "text"}}},"group": {"type": "keyword"}}}}
Indexing
PUT my-index-000001/_doc/1{"group" : "fans","user" : [{"first": "Robert","last": "Smith"},{"first": "Alain","last": "Robert"},{"first": "Robert","last": "De Niro"}]}
Searching
// match documents that have any user objects that match// first or last of "Robert"GET my-index-000001/_search{"query": {"nested": {"path": "user","query": {"match": { "user.*": "Robert" }}}}}// match documents that have individual user objects that match// first of "Robert" **and** last of "Robert"GET my-index-000001/_search{"query": {"nested": {"path": "user","query": {"bool": {"must": [{ "match": { "user.first": "Robert" }},{ "match": { "user.last": "Robert" }}]}}}}}
Vectors
Our migration to Elasticsearch unlocks some vector search options with the ability to map fields as dense and sparse vectors, by encoding vectors as binary doc_values. It is worth noting that lucene(opens in a new tab or window) (and hence both Elasticsearch and Solr) is adding features in this space, including Solr's recent support for HNSW Vector search(opens in a new tab or window).
Documentation and active community
Maintained docs and API references, as well as an active online community. As much as we appreciate the Apache mailing lists for Solr and Zookeeper, having online forums is a win.
Challenges when migrating
Dynamic fields
Dynamic fields are great if you want an unstructured search that lets you put anything into an index, but if you instead want a structured search with guaranteed fields, you must set this up before indexing.
Elasticsearch doesn't have a way to specify that all documents require a given field, or that a given field must have only one value, for that you would need an ingest pipeline with a fail processor.
You can't comment JSON
This seems like a small thing (and it probably is) but when going from
Solr's .xml schema to Elasticsearch's JSON templates, you must find a
new home for all your insightful annotations, such as reasons why we
don't want to lowercase username.
A visual view of index status
Another small thing, but coming from Solr, where it easy to get a graph and see which nodes are on which shard and their current status, Elasticsearch requires a different way of thinking to debug. If an Elasticsearch cluster is yellow, for example, you must debug this without the pretty picture.
The wonder of abstraction that makes the infra super easy to set up makes it harder to work out which node or instances are failing. We, fortunately, have had success in setting up dashboard with metrics by node and by index so that outliers can be spotted.
Additional files
You can upload extra files, such as those that contain synonyms, to a
collection and reference them by id. This id, however, is set on
upload and isn't mutable, or specifiable.
Just the beginning
These are the lessons learnt from migrating the first of our search engines to the Elasticsearch framework. We are now tackling bringing our larger and more set up services, with their full 7 years of patterns, over to Elasticsearch!
From our initial migrations, we're excited to not need to set up a Zookeeper with careful logging settings. We also appreciate all the learnings that our migration journey has taught us.
Acknowledgements
Kudos to all the people on search working on this migration:
- Ashwin Ramesh(opens in a new tab or window): who coordinated the whole migration effort.
- Josh Smith(opens in a new tab or window), Varun Chandola(opens in a new tab or window): who set up our modules and infrastructure.
- Brandon Janson(opens in a new tab or window), Nic Laver(opens in a new tab or window), Yiwei Han(opens in a new tab or window), Stuart Cam(opens in a new tab or window): who worked on our search platform, migrating key search components.
Interested in improving our search systems? Join Us!(opens in a new tab or window)


