Search
A content extension can be configured to include a search field. This allows users to find exactly the content they're looking for.
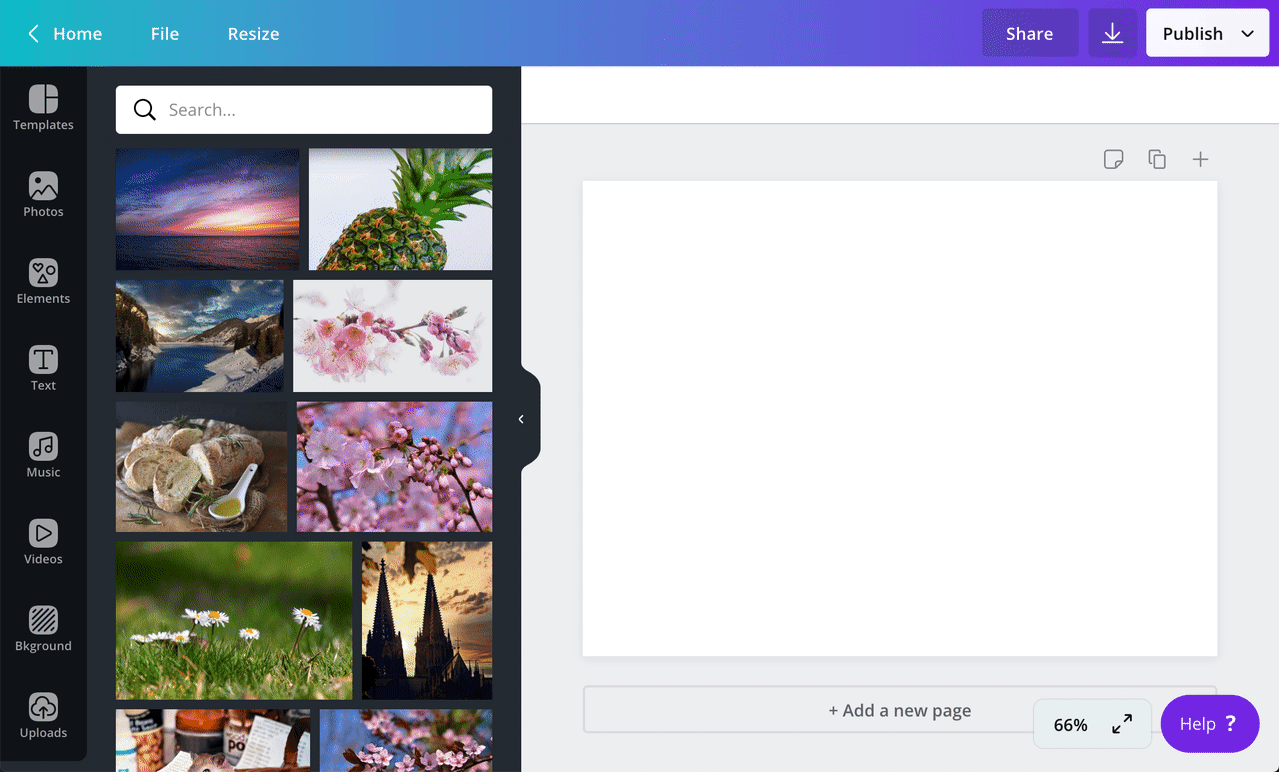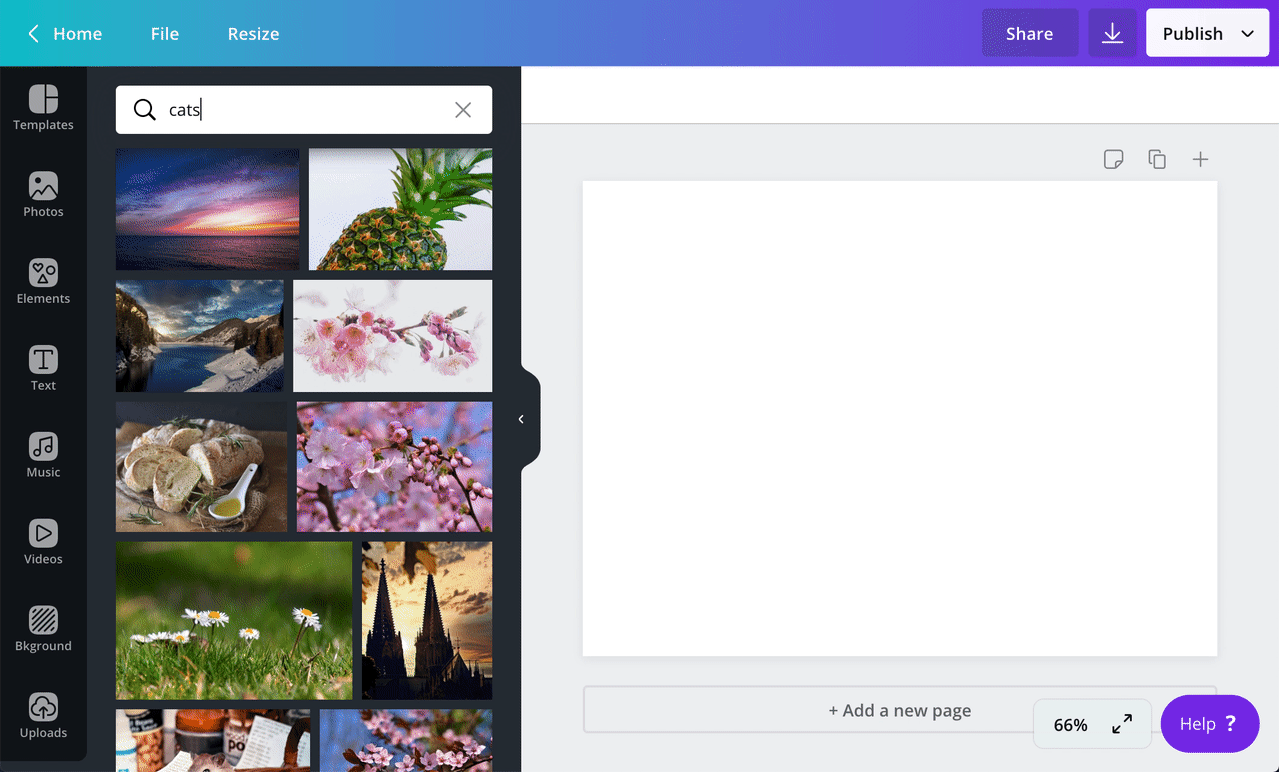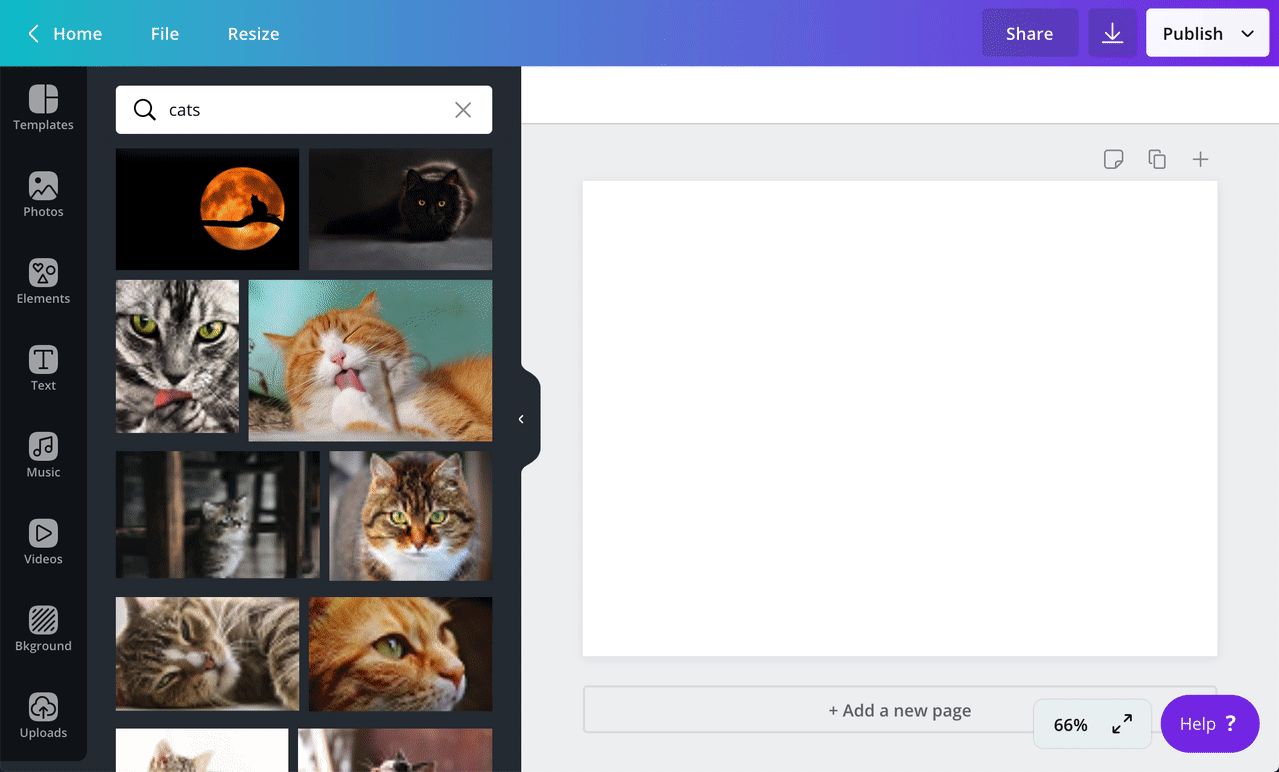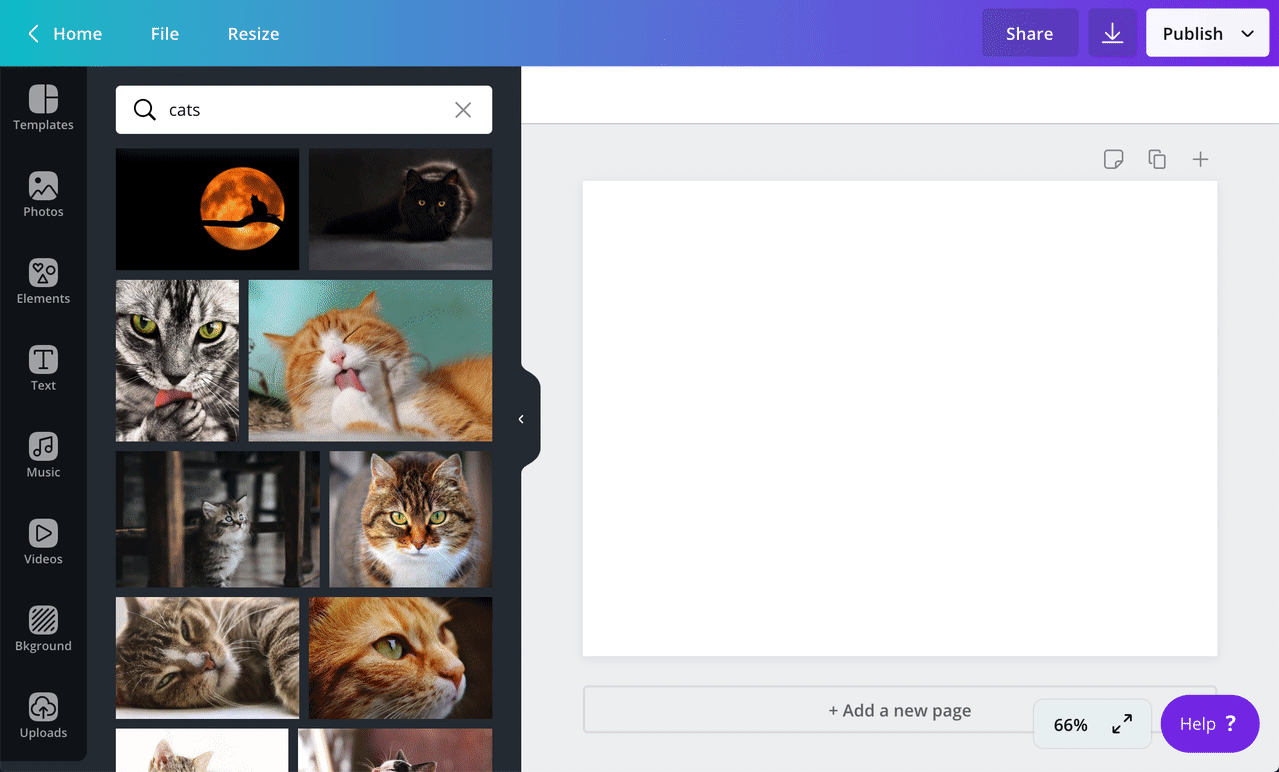
This topic explains how to receive and handle search queries.
Step 1: Enable search
By default, content extensions don't support search. You need to enable the feature.
For guidelines on providing the best search experience, see Add a search field to the extension.
To enable search for a content extension:
- Navigate to an app via the Developer Portal
- On the Extensions page, expand the Content panel.
- Select the Display search field checkbox.
Step 2: Receive search requests
When a user performs a search, Canva sends a POST request to the following URL:
<base_url>/content/resources/find
This is the same URL that Canva sends requests to when requesting images, embeds, and containers. The only difference is that the body of this request includes a query property that contains the user's search query:
{"user": "AUQ2RUzug9pEvgpK9lL2qlpRsIbn1Vy5GoEt1MaKRE=","brand": "AUQ2RUxiRj966Wsvp7oGrz33BnaFmtq4ftBeLCSHf8=","label": "CONTENT","limit": 100,"type": "IMAGE","locale": "en-US","query": "funny cats"}
Step 3: Detect when a user performs a search
When a POST request is not triggered by a search, the query property is null. You can therefore detect when a user has performed a search by checking if the value of the query property is null:
app.post("/content/resources/find", async (request, response) => {if (request.body.query) {// the user has performed a search}if (!request.body.query) {// the user has not performed a search}});
Step 4: Respond to search requests
When a user performs a search, a content extension should return a "SUCCESS" response that includes resources relevant to the user's query:
{"type": "SUCCESS","resources": []}
What counts as "relevant" depends on what you're trying to accomplish. Your extension could just return resources that have the user's exact search query in their name property. Or after users perform a search, you could keep track of what resources they drag into their designs and then use that data to surface the most relevant resources for future searches. It's your choice.
If a search returns more results than can be included in a single response, use pagination to load the additional resources.
Step 5: Handle containers
If an extension supports containers, it's important to know that the query and containerId properties are mutually exclusive. If the query property is not null, then the containerId will be null. This means a user cannot search within a container. You can, however, use a search query to return a filtered list of containers.
Example
This example allows users to search for photos from Pixabay(opens in a new tab or window). You'll need a (free) API key to run it.
const axios = require("axios");const express = require("express");const app = express();app.use(express.json());app.use(express.static("public"));app.post("/content/resources/find", async (request, response) => {// Configure the requestconst options = {url: "https://pixabay.com/api/",params: {key: process.env.PIXABAY_API_KEY,},};// If a user has provided a query, include it in the requestif (request.body.query) {options["params"]["q"] = request.body.query;}// Send a request to Pixabayconst pixabay = await axios.request(options);// Transform the array of images into an array of "IMAGE" resourcesconst images = pixabay.data.hits.map((image) => {return {type: "IMAGE",id: image.id,name: `Photo by ${image.user}`,thumbnail: {url: image.webformatURL,height: image.webformatHeight,width: image.webformatWidth,},contentType: "image/jpeg",url: image.webformatURL,};});// Return a "SUCCESS" responseresponse.send({type: "SUCCESS",resources: images,});});app.listen(process.env.PORT || 3000);