SearchableListView
SearchableListView is a UI component in the Apps SDK that helps users find your images, videos, embeds, and audio. It shows previews of your resources, and includes a search bar and customizable list filters.
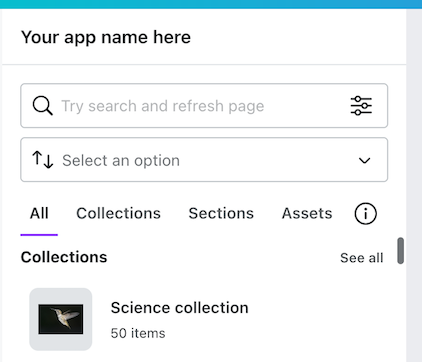
You can further customize this view, changing the container type, layout, and search options, among others. When a user clicks on a result, your app can trigger additional actions, such as adding the item to a design.
The following sections demonstrate some of the main features of SearchableListView, with examples of how you can customize them further.
Filter options
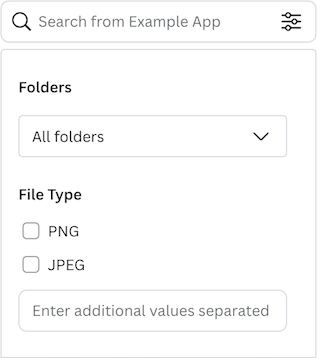
You can define the filters that let users narrow their search to specific filetypes:
{filterType: "CHECKBOX",label: "File Type",key: "fileType",options: [{ value: "mp4", label: "MP4" },{ value: "png", label: "PNG" },{ value: "jpeg", label: "JPEG" },],allowCustomValue: true,},
Example:
Sort options
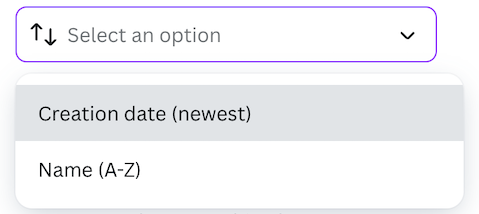
You can also define the sort options that users see.
sortOptions: [{ value: "created_at DESC", label: "Creation date (newest)" },{ value: "created_at ASC", label: "Creation date (oldest)" },{ value: "updated_at DESC", label: "Updated (newest)" },{ value: "updated_at ASC", label: "Updated (oldest)" },{ value: "name ASC", label: "Name (A-Z)" },{ value: "name DESC", label: "Name (Z-A)" },],
Example:
Layout
You can define how results are presented to users, using a list, masonry, or full width layout.
List
This option presents the results in a list view:
layouts: ["LIST"],
Example:
Masonry
This option presents the results in a masonry layout:
layouts: ["MASONRY"],
Example:
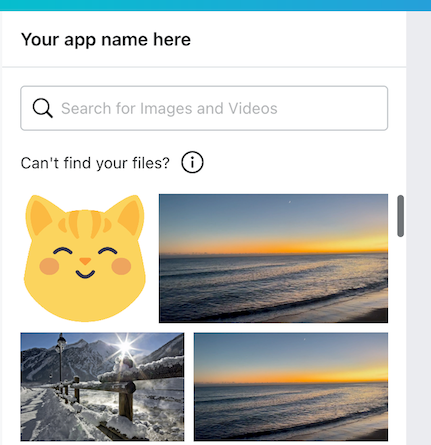
For a working example, see the Giphy app(opens in a new tab or window).
Full width
This option presents the results in a full width layout:
layouts: ["FULL_WIDTH"],
Example:
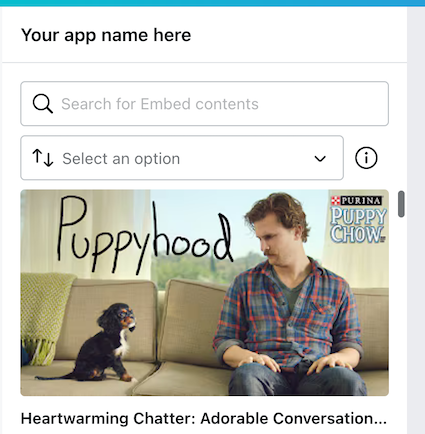
For a working example, see the YouTube app(opens in a new tab or window).
Next steps
- For the full list of SearchableListView customization options and their combinations, see the reference documentation(opens in a new tab or window).
- To add infinite scrolling to the SearchableListView component, see the example below.
Example: Infinite scrolling
To help resources load quickly, the SearchableListView(opens in a new tab or window) component limits how many resources can be returned in a single response.
If your app offers more resources than this limit allows, you can use multiple requests to load additional resources. This is commonly known as pagination and the Apps SDK calls it continuation.
This article explains how to enable infinite scrolling for the SearchableListView component, using an example digital asset management(opens in a new tab or window) app. This app is maintained by Canva and already has pagination configured.
- The backend retrieves images from Lorem Picsum(opens in a new tab or window), a service that provides placeholder photos.
- The frontend uses the SearchableListView(opens in a new tab or window) component to present the resources to users.
- To retrieve the next page of resources, the backend uses the
continuationproperty.
Step 1: Configure the service
-
In your backend code, create a basic Node.js server (using Express), and import modules for handling the Canva app components and HTTP requests:
import {FindResourcesRequest,FindResourcesResponse,Image,} from "@canva/app-components";import axios from "axios";import express from "express";import cors from "cors";const app = express();app.use(express.json());app.use(express.static("public"));app.use(cors());TYPESCRIPT
Step 2: Load the first page of resources
To retrieve the resources that will appear in the side panel, SearchableListView sends a POST request to the location you defined in findResources(opens in a new tab or window). This example uses /content/resources/find.
Example frontend code:
findResources={async (request) => {const response = await fetch("http://localhost:3000/content/resources/find",{method: "POST",headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json",},body: JSON.stringify(request),});
Example backend code:
app.post("/content/resources/find", async (req, res) => {const findResourcesRequest: FindResourcesRequest = req.body;const currentPage = findResourcesRequest.continuation || "1";
The following steps demonstrate how to retrieve the first page of resources and format the results.
-
To retrieve a list of images from Lorem Picsum, send a
GETrequest to this URL:https://picsum.photos/v2/listBASHThe response contains an array of images, with each image represented in the following structure:
{"id": "0","author": "Example author","width": 5600,"height": 3700,"url": "https://unsplash.com/...","download_url": "https://picsum.photos/..."}JSON -
To retrieve a different page of images, append a
pageparameter to the URL:https://picsum.photos/v2/list?page=2BASH -
To perform the request, call the
requestmethod:const options = {url: "https://picsum.photos/v2/list",params: {page: currentPage,},};const picsum = await axios.request(options);TYPESCRIPT -
Convert the data into a format that Canva can process:
const images: Image[] = picsum.data.map((image: any) => {return {type: "IMAGE",id: image.id,name: `Photo by ${image.author}`,url: image.download_url,thumbnail: {url: image.download_url,},contentType: "image/jpeg",};});TYPESCRIPT
Step 3: Load the next page
Before a user reaches the end of the resource list, you can trigger an additional request to /content/resources/find. This lets you seamlessly load additional resources, creating the effect of infinite scrolling.
You can do this by adding a continuation property to the response. This example shows the continuation property with the nextPage value, which loads the next page of results once the first page has loaded. This value doesn't have to be a page number, and only needs to be a string.
const nextPage = (parseInt(currentPage, 10) + 1).toString();const findResourcesResponse: FindResourcesResponse = {type: "SUCCESS",resources: images,continuation: nextPage,};res.send(findResourcesResponse);});
This property tells SearchableListView(opens in a new tab or window) to send another POST request to /content/resources/find, before the user reaches the end of the list of resources. This property and its value is included in the request body.
After adding this change, scroll through the resources in the side panel. You'll notice that the same resources are loaded repeatedly, which is addressed in the following steps.
Step 4: Get the current page number
When a response contains a continuation property, that same continuation property is available in the body of the next POST request that's sent to /content/resources/find.
You can check this behavior by logging the value of findResourcesRequest.continuation:
console.log(findResourcesRequest.continuation);
When the first page of resources is loaded, there isn't a previous response because the continuation property is null. However, if you trigger another request by scrolling through the resources, the "2" value is logged. You can use this behavior to load unique resources for each request.
At the top of the route (before the options object), create a currentPage variable containing the value of the request body's continuation property. In addition, provide a fall-back value of "1" because the continuation property is null on the initial request.
const currentPage = findResourcesRequest.continuation || "1";
You can then update the page parameter in the options object to use the currentPage variable:
const options = {url: "https://picsum.photos/v2/list",params: {page: currentPage,},};
As a result of these changes, you can load the first and second pages of content into the side panel.
As you continue scrolling through the resources, you'll notice that the second page of images is repeatedly loaded. This occurs because the value of the continuation property is hard-coded as "2" in all responses; This is addressed in the following steps.
Step 5: Increment the page number
To load unique resources for every request, you need to increment the value of the continuation property.
Before the res.send method, create a variable that:
- Parses the number from the
currentPagevariable. - Increments the page number by one.
- Converts the result back into a string.
For example:
const nextPage = (parseInt(currentPage, 10) + 1).toString();
You can then provide this variable in the response:
const findResourcesResponse: FindResourcesResponse = {type: "SUCCESS",resources: images,continuation: nextPage,}res.send(findResourcesResponse);});
As a result, a unique set of resources is loaded for each request.
Step 6: Load the final page of resources
When reaching the final page of resources, don't provide a continuation property in the response:
res.send({type: "SUCCESS",resources: images,});
Alternatively, set the continuation property to null, which indicates that there are no more pages to load:
res.send({type: "SUCCESS",resources: images,continuation: null,});
Example backend code
Find the complete example for the backend below:
import {FindResourcesRequest,FindResourcesResponse,Image,} from "@canva/app-components";import axios from "axios";import express from "express";import cors from "cors";const app = express();app.use(express.json());app.use(express.static("public"));app.use(cors());app.post("/content/resources/find", async (req, res) => {const findResourcesRequest: FindResourcesRequest = req.body;const currentPage = findResourcesRequest.continuation || "1";const options = {url: "https://picsum.photos/v2/list",params: {page: currentPage,},};const picsum = await axios.request(options);const images: Image[] = picsum.data.map((image: any) => {return {type: "IMAGE",id: image.id,name: `Photo by ${image.author}`,url: image.download_url,thumbnail: {url: image.download_url,},contentType: "image/jpeg",};});const nextPage = (parseInt(currentPage, 10) + 1).toString();const findResourcesResponse: FindResourcesResponse = {type: "SUCCESS",resources: images,continuation: nextPage,};res.send(findResourcesResponse);});app.listen(3000);
Localization
The user-facing strings in the SearchableListView component will be automatically localized for all supported locales as long as your app has been otherwise localized in accordance with the recommended localization workflow.
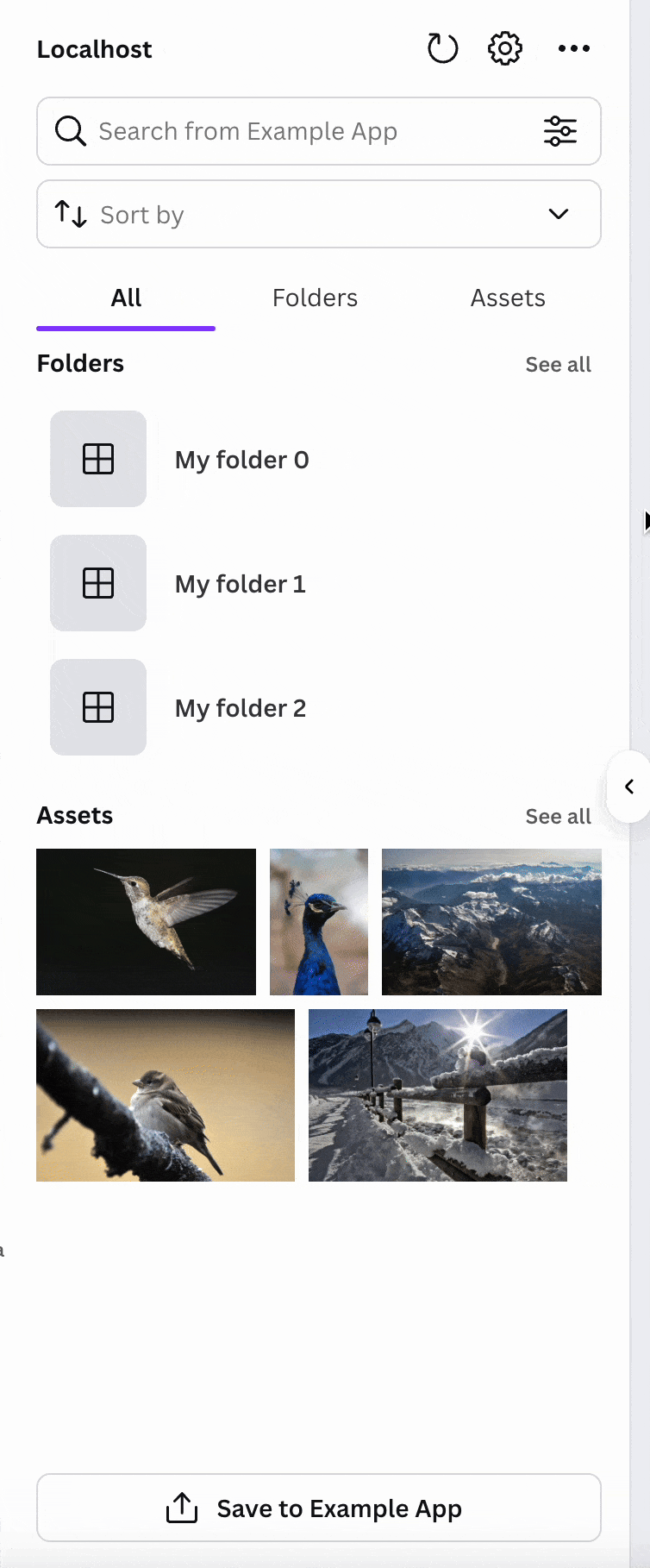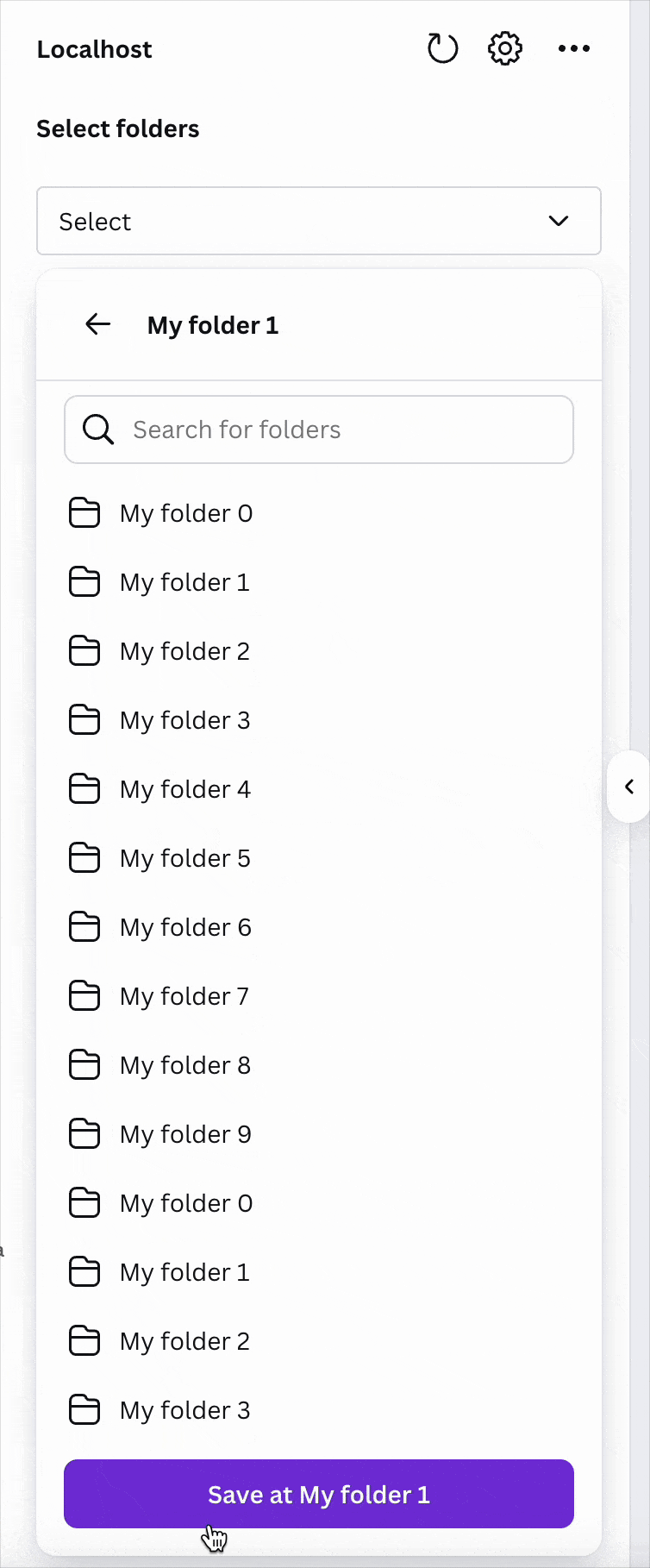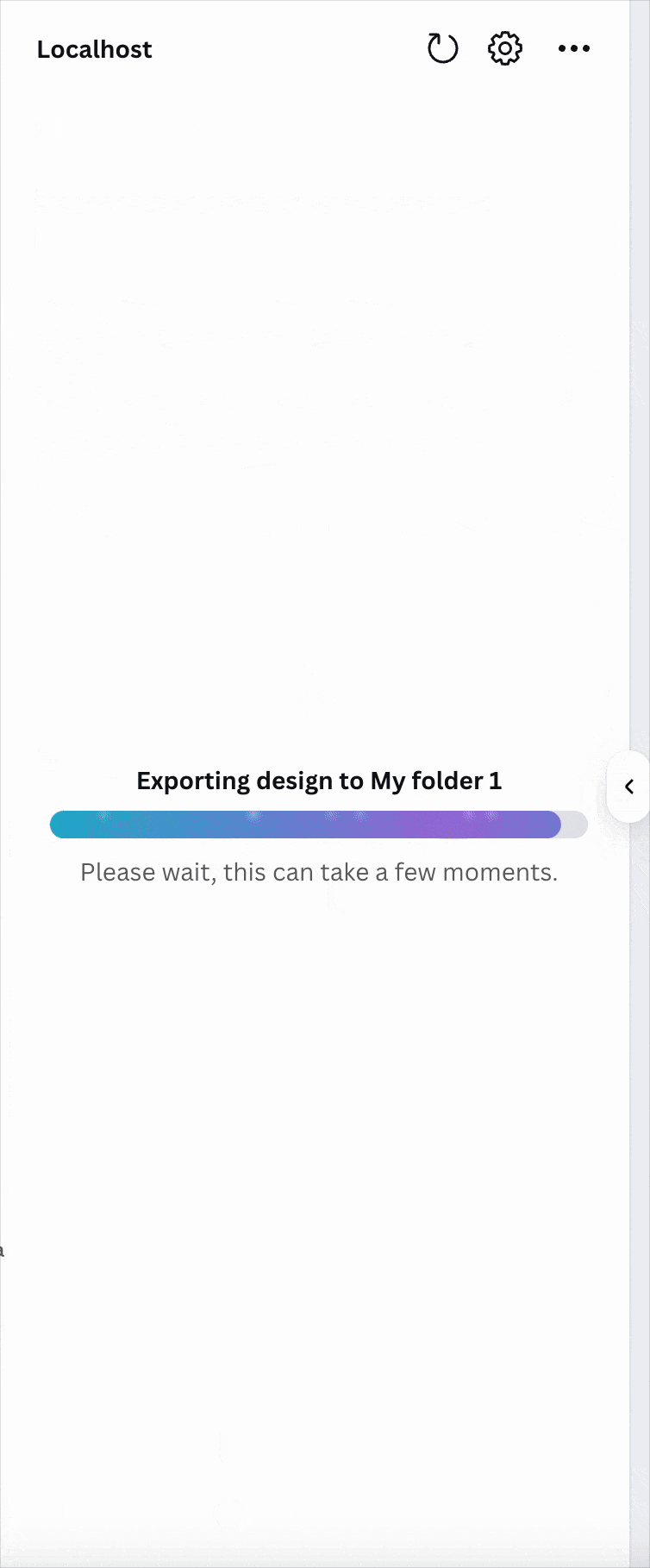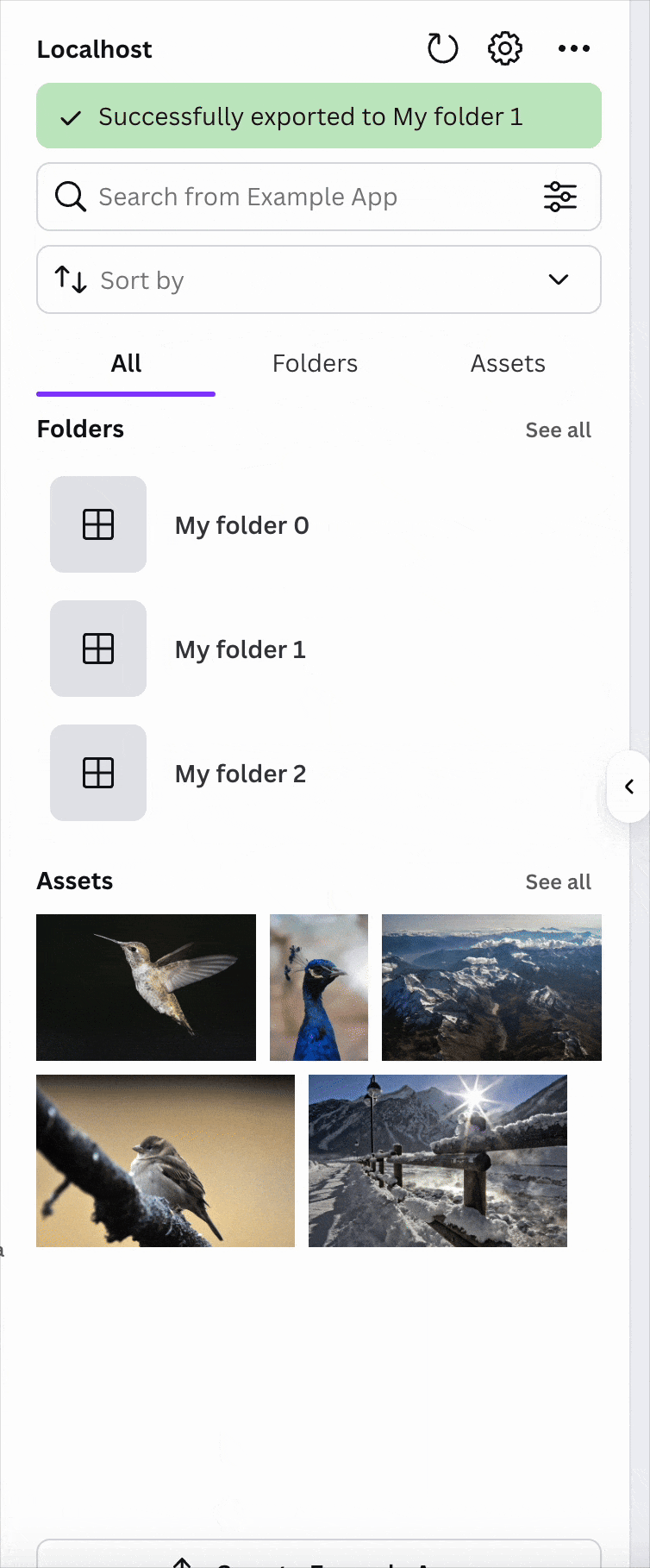
Export
Use the saveExportedDesign callback to export a Canva design to a third-party platform. You can do this by defining a function that uses saveExportedDesign, and setting your configuration to accept exports.
To export a Canva design to a third-party platform:
-
Enable exports in the
SearchableListViewconfig.tsfile:{export: {enabled: true,estimatedUploadTimeMs: 1500,acceptedFileTypes: ["gif", "jpg"]}}TSThe available options for the
exportproperty include:enabled: Set astrueto enable exports.acceptedFileTypes: Include a list of file types that can be exported.requireContainerSelected: Set astrueif you require users to select a container for the design before they can export it.containerTypes: Specify how the export container type is presented and managed (for example, a "folder" or "collection").estimatedUploadTimeMs: Set a value in milliseconds to adjust progress bar appearance and speed.
-
Add a
saveExportedDesignprop to the component:<SearchableListViewconfig={config}findResources={findResources}saveExportedDesign={(exportedDesignUrl: string,containerId: string | undefined,designTitle: string | undefined) => {return new Promise((resolve) => {setTimeout(() => {console.info(`Saving file "${designTitle}" from ${exportedDesignUrl}to ${config.serviceName}container id: ${containerId}`);resolve({ success: true });}, 1000);});}}/>TSX
This prop accepts a callback function that runs when the design has finished exporting. You can use this function to:
- Download the exported design file.
- Save the file to your service.
To see an example of how this callback is used, check out the DAM app template(opens in a new tab or window).
Example: